Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
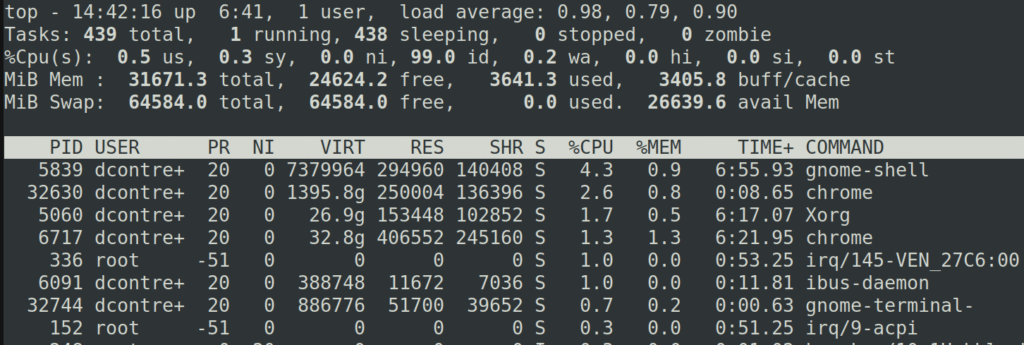
What is the load average metric, and what utilities can you use to check its value?
It is an estimate of the number of processes that are capable of using the CPU at any given time. This is quantified by the count of processes that are in either a runnable state (denoted as ‘R’, a process utilizing or awaiting CPU resources), or an uninterruptible sleep state process, also known as a blocking state (denoted as ‘D’, a process awaiting I/O operations to complete).
The system’s load average does not take into account the priorities and niceness of the processes that are running.
An acceptable load average depends on your system. Each host and workload is different. The load is displayed in a 1-minute, 5-minute, and 15-minute averages.
A good rule of thumb, is that the load average value, should not be higher than the number of CPU cores in your system.
For example, if you have a single core processor, then a 2 load average would mean that typically a process is using the CPU while another one waits.
A multi core higher than 2 will work without issues compared to the previous scenario. So, what’s normal for a host?
I would say, “high” means high enough that you don’t need uptime, top, htop, or any other utility to tell you that the system is overloaded, you can tell from its response time.